
 nootro
nootro

 2017-10-16
2017-10-16
 0
0
 9317
9317
Bavachinin (BVC) a novel natural pan-PPAR agonist from the fruit of the traditional Chinese glucose-lowering herb Malaytea scurfpea fruit, the seed of Psoralea corylifolia Linn. Natural herbs provide a structurally untapped resource to prevent and treat complicated metabolic syndrome. The metabolic syndrome is a cluster of metabolic abnormalities, including type 2 diabetes, obesity, dyslipidaemia, insulin resistance, liver steatosis and hypertension. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) belong to the nuclear receptor superfamily that function as ligand-inducible transcription factors and control the expression of multiple target genes.
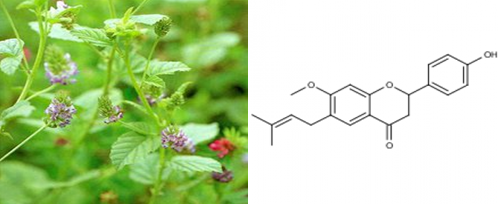
Pan-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) agonists have long been sought as therapeutics against the metabolic syndrome, but current PPAR agonists show limited efficacy and adverse effects. BVC synergised with thiazolidinediones, which are synthetic PPAR-γ agonists, and fibrates, which are PPAR-α agonists, to induce PPAR transcriptional activity, as well as to lower glucose and triacylglycerol levels in db/db mice. BVC exhibited glucose-lowering properties without inducing weight gain and hepatotoxicity.
BVC-Reduce weight gain
In order to prove that Bavachinin can significantly reduce weight gain, Scientists conducted the following tests. They evaluated the glucose- lowering effects of BVC in leptin-receptor-deficient db/db mice and DIO mice. Test results can refer to the following figure data.
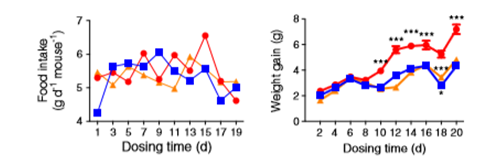
In groups of db/db mice with similar food intake, RSG greatly increased body weight by approximately 8 g within
3 weeks (p<0.001), whereas BVC treatment did not significantly induce weight gain.
So why dose Bavachinin offset the fat accumulation to reduce the weight gain?
Increased fatty acid oxidation, reduced fatty acid uptake and synthesis, and increased lipid movement in adipose tissue. The activation of Bavachinin can increase the fatty acid burning capacity of skeletal muscle, along with the redistribution of fatty acid flux to adipose tissue into skeletal muscle.
BVC --glucose-lowering effects without hepatotoxicity.
Hepatotoxicity: Damage or injury to the liver caused by a drug, chemical or other agent. Symptoms vary depending on the degree of exposure and hence extent of the liver damage or injury. Mild liver damage may cause few if any symptoms whereas severe damage can ultimately result in liver failure.
Liver as an important organ of drug metabolism, most of the drugs into the body, will be metabolized by the liver and then absorbed by the body. So the liver is the source of drug damage caused by one of the main target organs, more susceptible to drug damage. So the more important point is that Bavachinin in the process of lowering glucose does not cause hepatotoxicity.
To reveal the mechanism underlying BVC-mediated improvement in the metabolic syndrome, liver gene expression profiles of db/db and DIO mice were analysed by cDNA genome-wide gene expression assay. Test results can refer to the following figure.
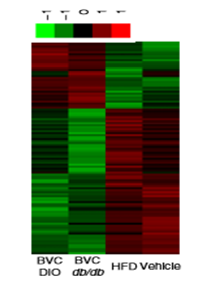
The figure shows the 138 overlapping differential genes of both mouse livers that were identified(fold change ≥2, p<0.05). Gene ontology pathway and hierarchical cluster analysis further revealed the most enriched pathways regulated by BVC were related to adipocytokine signalling, PPAR signalling, type 2 diabetes, glycerophospholipid metabolism, mitochondrial fatty acid beta oxidation and butanoate metabolism.
In conclusion, the synergistic effects occur because of the unique binding events of BVC to PPAR-α and -γ. Therefore, the combination of natural BVC plus TZDs or fibrates could help increase effectiveness with fewer doses, followed by controlled side effects. This discovery may provide a new promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and other metabolic syndrome indications. This is the first report of a synergistic glucose- and lipid-lowering effect of BVC and synthetic agonists induced by unique binding with PPAR-γ or -α. This combination may improve the efficacy and decrease the toxicity of marketed drugs for use as adjunctive therapy to treat the metabolic syndrome.
Diabetes, often referred to by doctors as diabetes mellitus, des... More

 0
0

 0
0
According to research, myricetin stimulates glucose transport in... More

 0
0

 1
1
There are many studies at the molecular, biochemical, organism a... More

 0
0

 0
0
In vivo, betaine acts as a methyl donor for the conversion of h... More

 0
0

 0
0
Apigenin, an abundant dietary flavonoid, is emerging as a potent... More

 0
0

 0
0
BVC synergised with thiazolidinediones, which are synthetic PPAR... More

 0
0

 0
0
Epicatechin is an antioxidant flavonoid, occurring especially in... More

 6
6

 2
2
Fatigue is a very common phenomenon. There are many reasons can ... More

 2
2

 1
1
There are some simple steps can be taken to prevent or slow bone... More

 0
0

 0
0
Echinacea is also called the magic herb that can bring health to... More

 0
0

 0
0
Obesity has become a global health issue. It is a medical condit... More

 0
0

 0
0
Cardiac hypertrophy is the myocardial response to various pathol... More

 7
7

 1
1
Aging is becoming an international challenge to healthcare syste... More

 0
0

 0
0
Studies have shown that this compound possesses a plethora of b... More

 0
0

 0
0
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways... More

 0
0

 0
0
